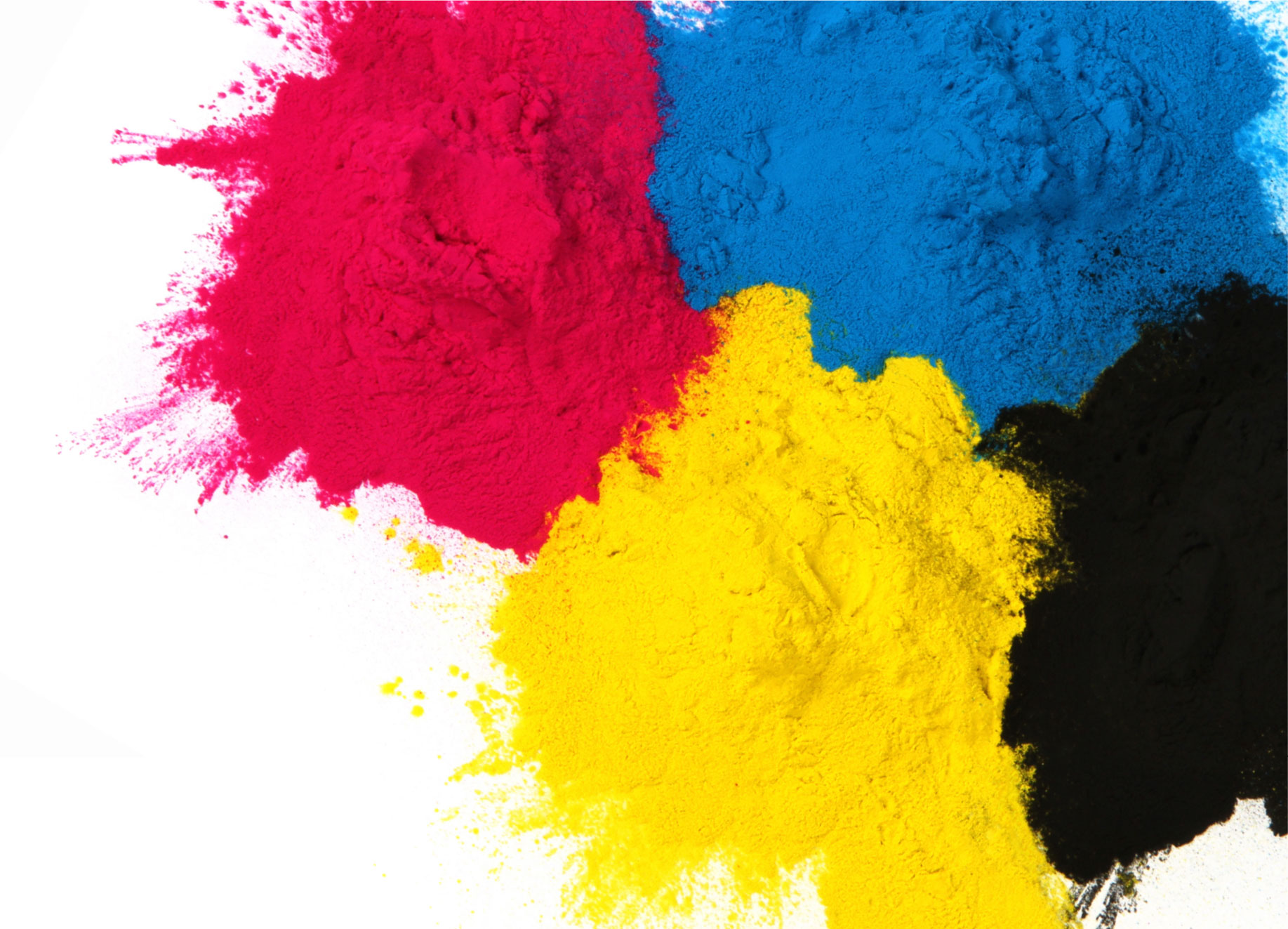
The four-color process consists of dividing an original (analog or digital) in 4 color channels: yellow (y), magenta (m), cyan (c) and black (k).

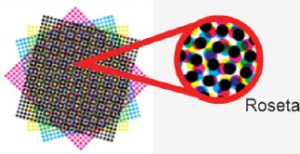
The printing is done through frames. A plot is a sequential in rows and columns of points. Overcoming these frames in different angles is interpreted as the formation of different colors, leftovers, and gradients. The point where these frames converge is called a rosette. When the frames converge on the same angle, a color plaster called moire is formed.
This means that we can use a lot of colors in our design, since these will be separated into cmyk percentages. It is important to stand out that RGB colors and most Pantone ® colors cannot be reproduced in CMYK, unfortunately most of the digital printing systems print in CMYK, however process printing is widely used in printing systems such as Offset.
Color separation of or direct inks

It is when we separate or divide an original (analogue or digital) in 2 or more colors, usually taking as a reference the pantone, since in some printing systems such as serigraphy, there are not many available colors in the inks as there are colors in the pantone, so in that case, it will be only used as a reference.

A pantone is a catalog of colors. There are different types depending on the substrate and the ink, with which it is printed, is a reference to avoid color variation. A color selection or printing in direct ink, is ideal for managing corporate colors, where the designs are direct, which means without gradients, and are usually located in logos or in specific parts of the design that link it in a direct way with your brand.

Inks
An ink is a homogeneous mixture of coloring matter, resins, solvents and some additives whose its function is to reproduce an image over a support by a printing process. The composition in quantity and variety of the components is determined by the function of the type of ink and the properties that have been released according to their use.

The inks are formed by:
a) Coloring substances that also may be:
a1. – Inks or dyes that are soluble substances in the vehicle.
a2. – Pigments: substances that are not soluble in the vehicle and that do not exist disperse in the form of particles.
b) Vehicles: the link, in which the dye is dissolved or dispersed to the pigment, is called a vehicle.
The vehicle is responsible for transporting the colored matter from the printing machine to the support, in addition to fulfilling its mission to disperse or dissolve.
When the ink comes in contact with the support, the vehicle works as a homogenous agent, that means, assures the dye or the pigment over the support, through the dry process.

